Adi Tarka
Parama pujya Sri Ramakrishna Guruji for sake of beginners has simplified Tarka Sangraha and presented in a simple lucid manner. I have attempted in following pages to explain Adi Tarka based on his lectures.
Tarka is a comprehensive text for both Nyaya and vaisheshika school.
The premise of tarka sangrah is how to classify things. All the philosophies have one basic principle that is to give you realization. So, logicians accept realization can only be gained by categorizing things. Means if you can categorize things then there will be no fear meaning you are realized.
Padarta – Substance
Logicians accept 7 substances. Namely
- Dravya (Things) – 9
- Guna (attributes) -24
- Karma (Action) -5
- Samanya (Class/Generality/Species) -2
- Vishesha (Specialty/particularity) – Infinite
- Samavaya –(relationship between two inseparable things /inherence) 1
- Abhava (absence) – 4
Shastra pravrutti
- Uddesha -Defined नाममात्र वस्तु संकीर्तनम् Naming an object is called Uddesha. Example: गौ (cow)
- Lakshana – Definition असाधारणधर्म example : Lakshana of cow is सास्नादिमत्वम् (dewlap)
- Pariksha – लक्षितस्यलक्षणं भवति नवा इति विचारः – Whether the definition for the defined is right or wrong.
While doing Pariksha we check for below 3 doshas (defects), that means the definition should be devoid of these three doshas.
- Avyapti – लक्ष्यैकदेशवृत्तित्वमव्याप्तिः– The definition only accounts for a portion of the defined. For example, if we define cow as ‘कपिलत्वम्’ (i.e Blackness is cowness) then this definition will not cover other colored cows.
- Ativyapti – लक्ष्यवृत्तित्वेसति अलक्ष्यवृत्तित्वम् – The definition fits in the defined but it also fits in the not defined. For example, if we define cow as the one which has horn शृग़ित्वम्. This will also cover other animals like deer etc.
- Asambhava – लक्ष्यमात्रावृत्तित्वमसम्भवः- Having nonexistence in the defined. Ex: if you define cow as the one having single hoof. Then definition will not holds good for cow.
Pratiyogi and Anuyogi
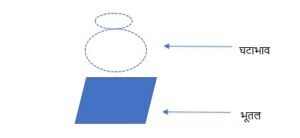
प्रतियोगि : यस्य अभावः : Of which you see the absence is pratiyogi. In the below example
We are talking about absence of pot (घटाभाव), pot is the pratiyogi in this example.
अनुयोगि : यस्मिन् अभावः :On which you see the absence is anuyogi. In the below picture भूतल is the anuyogi.
द्रव्य – Dravya (Things)
Note different school of logic accepts different number of dravyas. Here we are accepting 9 dravyas.
पृथिव्यप्तेजोवाय्वाकाशाकालदिगात्ममनांसि नवैव
- पृथिवी – Earth : गन्धवती पृथिवी that which has odor is Earth.
पृथिवी is of two types
- Nitya – नित्या परमाणुरूपा ie the atom. Nitya can be defined as ध्वंसाप्रतियोगि that which is not an object of destruction.
- Anitya – अनित्या कार्यरूपा, Again Anitya is of 3 types
- Sharira – शरीरमस्मदादीनाम्, like our body.
- Indriya – नासाग्रवर्ति – tip of nose
- Vishaya – विषयो मृत्पाषाणादिः – mud, clay, stone etc.
- आपः – Water शीतस्पर्शवत्यः that which is cold to touch is water.
आप is of two types
- Nitya – परमाणुरूपा
- Anitya – कार्यरूपा Again Anitya is of 3 types
- Sharira – शरीरं वरुणलोके – Varuna loka
- Indriya – जिह्वाग्रवर्ति – Taste buds
- Vishaya – विषयो सरित्समुद्रादिः – river, ocean etc
- तेज – Fire उष्णस्पर्शवत्तेजः that which is hot to touch is Fire.
तेज is of two types
- Nitya – परमाणुरूपा
- Anitya – कार्यरूपा Again Anitya is of 3 types
- Sharira – शरीरमादित्यलोके प्रसिद्धम् – Aditya (Sun) loka
- Indriya – कृष्णताराग्रवर्ति – That which is in the center of pupil – Vision
- Vishaya भौमदिव्यौदर्याकरज भेदात् is of 4 types
- भौम – वह्न्यादिकम् – For which earth itself is the fuel.
- अबिन्धन – विद्युदादि – For which water is the fuel like Lightning.
- औदर्य – भुक्तस्य परिणामहेतुरौदर्यम् – For which both earth and water are the fuel like in the stomach that which helps digestion.
- आकरज – सुवर्णादि – that we gain by mining like gold etc.
- वायुः – Air रूपरहीतः स्पर्शवान्वायुः that which is cold to touch is water.
आप is of two types
- Nitya – परमाणुरूपा
- Anitya – कार्यरूपा Again Anitya is of 3 types
- Sharira – शरीरं वायुलोके– Vayu loka
- Indriya – त्वक्सर्वशरीरवर्ति – touch
- Vishaya – विषयो वृक्षादिकम्पनहेतुः – Tree shaking etc.
शरीरान्तःसंचारी वयुः प्राणः: This is the internal air. The prana gains different names based on different functionalities
- Prana
- Apana
- Vyana
- Udana
- Samana
- आकाश- Space- शब्दगुणकमाकाशम् that which has the attribute/quality of sound.
तच्चैकं विभु नित्यञ्च Akasha is accepted to be
- एकम् – one(therefore there is no class/jati)
- नित्या – nitya ध्वंसाप्रतियोगि
- विभु – सर्वमूर्तद्रव्यसंयोगि – that which has association with all the manifest substances. All pervading.
- कालः – Time अतीतादिव्यवहारहेतुः – Through which you have the transactions like past,present and future is called Kaala.
This is also accepted to be
- एकम्
- नित्या
- विभु
- दिक् – Direction प्राच्यादिव्यवहारहेतुर्दिक् – – Through which you have the transactions like East, west, North, south etc. takes place is called Dik.
This is also accepted to be
- एका
- नित्या
- विभ्वी
- आत्मा – Atma ज्ञानाधिकरणमात्मा – That which is the substratum for knowledge is atma.
This is of two types
- जीवात्मा – प्रतिशरीरं भिन्नो विभुर्नित्यश्च – That which is different in each body, Jivatma is eternal, manifold and all pervading.
- परमात्मा – तत्रेश्वरः सर्वज्ञः परमात्मैक एव – Paramatma is Eswara, there is only one Eswara. And all knowing (सर्वज्ञः).
We accept transactions Jnana, iccha and kriya. These transactions in Jivatma is limited. However, in Paramatma it is unlimited.
- मनः – Mind सुखाद्युपलब्धिसाधनमिन्द्रियं मनः – The sense organ which is the means to gain happiness etc. is called the Mind.
Mind is
अनन्तम् – manifold, unlimited like Jivatma
परमाणुरूपा – It is of the size of atom,
नित्यम् – Eternal
कर्म – Karma (Action)
कर्म – Karma चलनात्मकं कर्म That which has movement is called Karma.
Even though Karma is one, it is differentiated into 5 types.
उत्क्षेपन -ऊर्ध्वदेशसंयोगहेतुरुत्क्षेपणम् – Going to higher by giving up the lower area is called utkshepanam.
अपक्षेपन – अधोदेशसंयोगहेतुरपक्षेपणम् – Going to lower by giving up the higher area is called apakshepanam.
आकुञ्चन – शरीरसंनिकृष्टसंयोगहेतुराकुञ्चनम् – Coming towards yourself.
प्रसारण – विप्रकृष्टसंयोगहेतुः प्रसारणम् – Going away from yourself.
गमन – अन्यत्सर्वं गमनम् – All other movements are called Gamanam.
सामान्यं – Samanya (Class/Generality/Species)
सामान्यं – Samanyam- नित्यमेकमनेकानुगतं सामान्यं – Logician accepts Samanyam as Jathi (means Class or species or Genre)
नित्यम् – Eternal
एकम् – one
अनेकनुगतम् – part of many
Take one example गो (cow ), गोत्व (cowness) is part of all the cows. So गोत्व is the Samanyam. Even if you destroy the cow, Cowness cannot be destroyed. Therefore Samanyam is Eternal. Same cowness exist in all the cows therefore अनेकनुगतम्.
Samanyam is of two types
पर Para परं सत्ता – means existence
अपर Apara अपरं द्रव्यत्वादिः – Liquidness etc
विशेष- Vishesha (Specialty/particularity)
विशेष – Vishesha नित्यद्रव्यवृत्तयो व्यावर्तका विशेषाः – That which exist in eternal Dravya and that which is distinguishing one from other.
समवायः – Samavaya –(relationship between two inseparable things /inherence)
समवायः – Samavaya नित्यसम्बन्धः समवायः – The relationship that exists eternally is called Samavaya.
Example : Say we have a whiteboard, the whiteness cannot be separated from the board. This relationship is called Samavaya. That is why it is called अयुतसिद्धवृत्तिः which means one dependents on the other till its extinction.
In all the below examples we have Samavaya Sambandha
अवयव – अवयवी
जाति – व्यक्ती
गुण – गुणी
अभाव – Abhava (absence)
अभावश्चतुर्विधः प्रागभावः प्रध्वंसाभावः अत्यन्ताभावः अन्योन्याभावश्चेति
प्रागभावः प्रध्वंसाभावः अत्यन्ताभावः can be classified as संसर्गाभाव
- प्रागभावः : अनादिः सान्तः प्रागभावः उत्पत्तेः पूर्वं कार्यस्य ||
This has no beginning but has end. Before the creation of an object pragabhava exists. For example, from when did the absence of pot existed? it is beginningless, when it was ended? When the pot is created.
- प्रध्वंसाभावः : सादिरनन्तः प्रध्वंसः उत्पत्यनन्तरं कार्यस्य |
This has a beginning but no end. When the pot is destroyed, there is a beginning of the destruction but no end, destroyed pot can’t be destroyed again.
- अत्यन्ताभावः : त्रैकालिकसंसर्गावच्छिन्नप्रतियोगिताकोऽत्यन्ताभाव |
Absence in all the 3 periods of time, past, present and future can be in 3 seconds. There was a absence of pot last 1 sec ago, there is absence of pot now and there is absence of pot in next second. Eg: यथा भूतले घटो नास्तीति
- अन्योन्याभाव : तादात्म्यसम्बन्धावच्छिन्नप्रतियोगिताकोऽन्योन्याभावः ।
Absence of one in other, like there is no Pot in Cloth. (यथा घटः पटो नेति )
